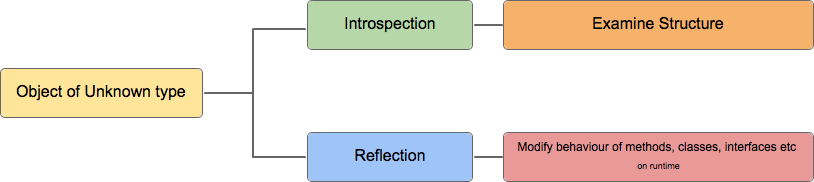
Java Reflection is the process of analyzing and modifying all the capabilities of class at runtime. Reflection API is used to manipulate class & its fields, methods, and constructor at run-time. Reflection in Java The java.lang.reflect package provides many classes to implement reflection. Methods of java.lang.Class is used for extracting the complete metadata of a class. Classes in java.lang.reflect package: As per the Oracle's document, following is the list of various java classes in java.lang.reflect
Read more 0Programming
Application development using different tools, technologies, platform and programming languages.
In Java volatile keyword is used to guarantee memory visibility of a variable. When a variable is marked as volatile, it will be stored in main memory. Every read & write is performed on main memory instead of CPU cache. In case of without volatile instance variable, read/write are always performed on CPU cache not directly on main memory, in such cases when multiple threads are performing read/write on multiprocessor system there are possibilities that
Read more 0In mathematical logic, a predicate is commonly understood to be a Boolean-valued function P: X→ {true, false}, called the predicate on X. Informally, a predicate is a statement that may be true or false depending on the values of its variables. It can be thought of as an operator or function that returns a value that is either true or false. For example, predicates are sometimes used to indicate set membership: when talking about sets,
Read more 0Java has always been an Object Oriented programming language, it means we can't have a function without its class. Other programming languages like C++, PHP, Python, JavaScript and many more, where we write functions and use anywhere, all these languages support functional programming along with Object Oriented programming. Java introduced Functional interface & Lambda Expressions in Java 8, to leverage functional programming to reduce verbosity. What is functional Interface? A Functional Interface is an interface
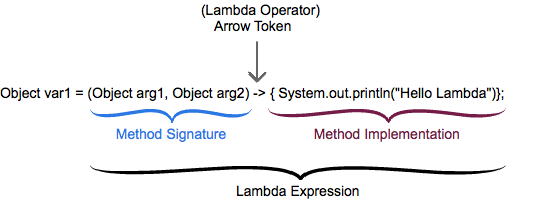
Read more 1Lambda expression is a concise representation of an anonymous function which can be passed as an argument to a method or stored in a variable. We call it anonymous function because it isn't associated with a particular class like a method does and it doesn't have a explicit name like a normal method. Like any regular method a lambda has a list of parameters, body, return type and list of exceptions which can be thrown.
Read more 0